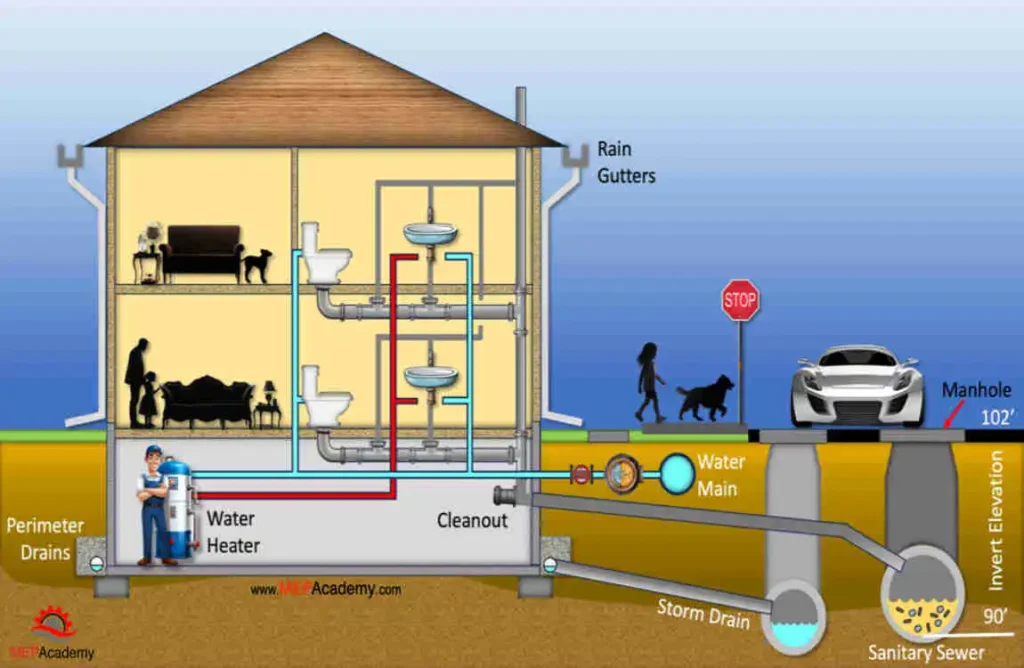
A house plumbing plan is like a detailed map that shows how water flows in and out of a home, including water supply lines, drainage, vents, and plumbing fixtures. Understanding how to read these plans step-by-step helps homeowners, builders, and plumbers ensure that the plumbing system is efficient, compliant with codes, and correctly installed without costly mistakes. This guide will walk through the basics of reading plumbing plans—from interpreting symbols and layouts to tracing water and waste lines for a clear, manageable understanding of the house plumbing blueprint.
Understanding the Basics of House Plumbing Plans
Before diving into the map-like complexity of plumbing plans, it helps to understand what precisely these documents are and why they matter.
What Are Plumbing Plans, Anyway?
Plumbing plans are detailed architectural drawings that show the location of pipes, fixtures, vents, and other components of a home’s water and waste systems. Imagine them as instruction manuals for your home’s veins—they tell you how clean water flows in and how wastewater exits. Unlike general blueprints, plumbing plans focus exclusively on pipes, traps, and connections.
What Do These Plans Typically Include?
A standard house plumbing plan will outline:
- Fixtures (showers, sinks, toilets).
- Supply lines (water coming into the house).
- Drain-Waste-Vent (DWV) tubes (wastewater removal and airflow).
- Main networks and individual branch connections.
- Valves, traps, and cleanouts (for maintenance access).
These details are standardized across most plans, though specifics may vary by region or builder.
Key Symbols and Notations Used in Plumbing Plans
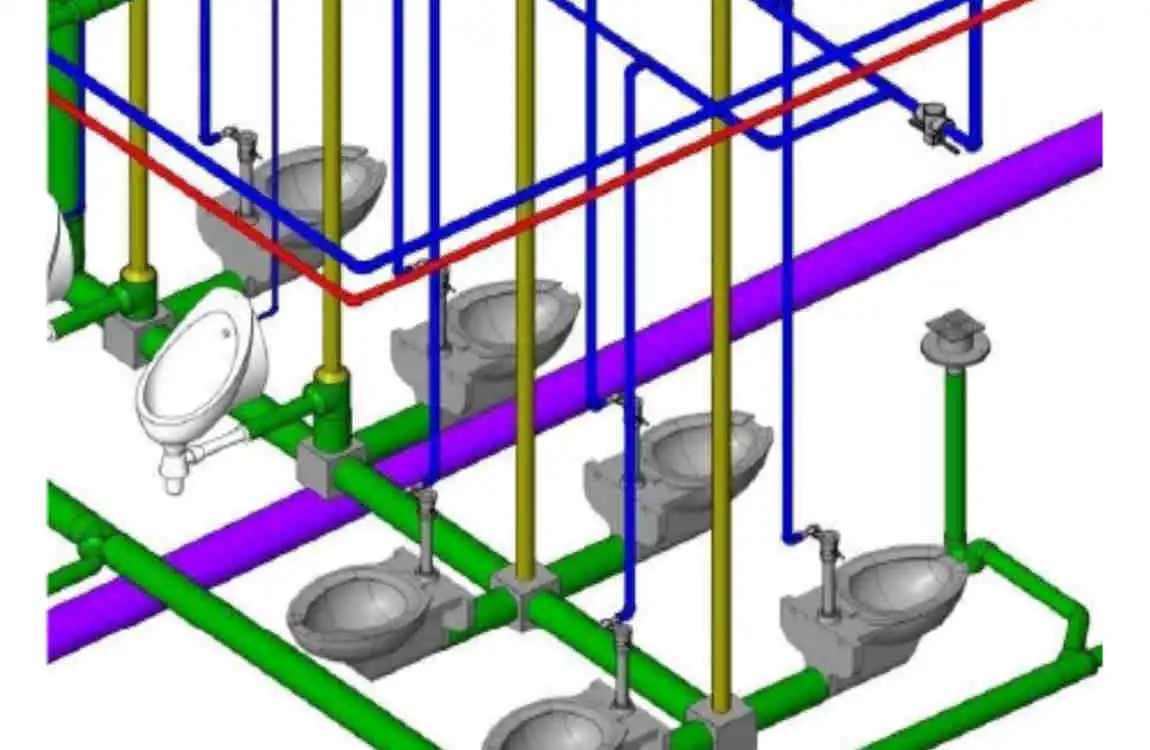
One of the biggest hurdles? Plumbing symbols—those mysterious doodles that look like abstract art. But once you know them, these icons are like decoding a secret language.
Common Symbols to Know
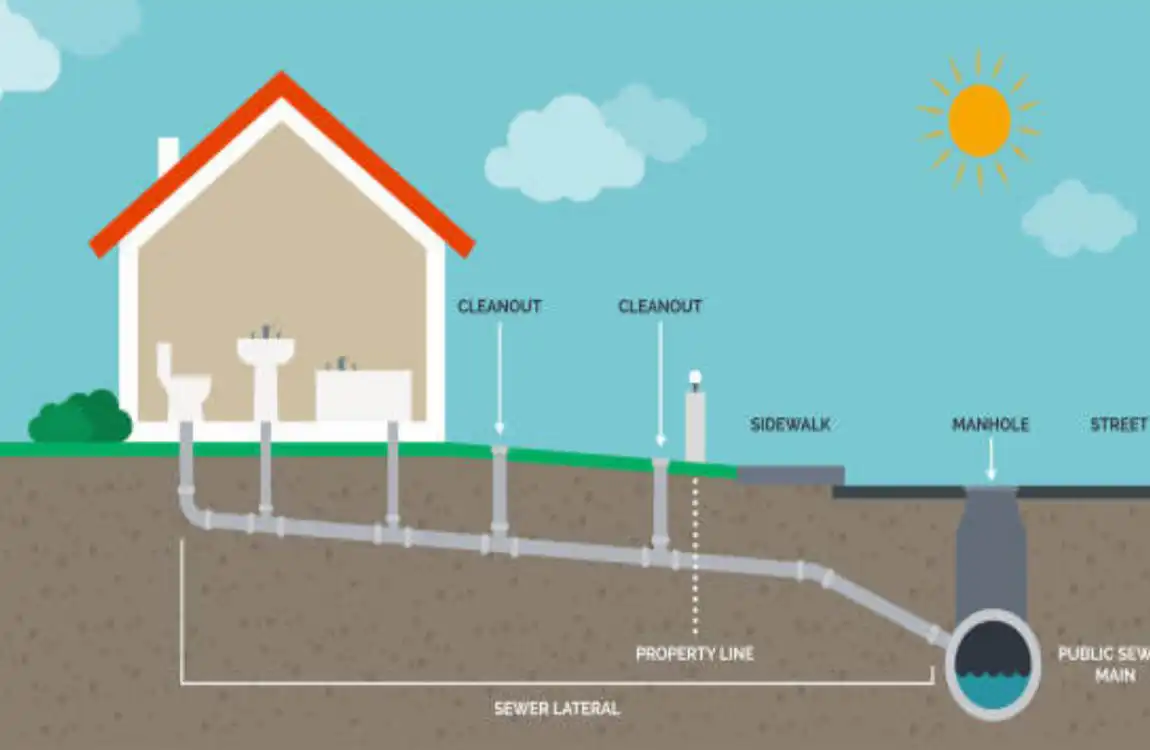
Here’s a quick breakdown of essential symbols:
SymbolMeaning
Circle with “W” labeled Water supply line
Dotted or dashed line, Drainpipe or gas line
Starburst icon Water heater location
Triangle outline Floor or roof drain
Plus sign Shower or faucet
Plumbers designers adhere to national standards for these marks, such as the ASME Y14.8-2020 standards in the U.S., so you won’t usually guess their meaning. Think of it as learning road signs—you may feel lost now, but once you understand, the system makes sense.
Pipe Sizes, Directions, and Fixtures at a Glance
You’ll often see pipes labeled with diameters like “1.5” PVC” or “1” Copper.” The direction of flow is usually marked by small arrows, while abbreviations like “DWV” (Drain-Waste-Vent) appear for complex systems.
Tip: Label colors matter too in digital plans! Red might indicate hot water pipes, while blue often represents cold water. Gray or black lines likely mark drains. Always check the legend!
Tips for Learning Symbols Faster
Struggling to memorize symbols? Practice makes perfect! Try these tricks:
- Flashcards: Visual recall is powerful.
- Print out symbol charts: Stick them to your wall or workspace.
- Use an app or cheat sheet: Many free resources exist for on-the-go learning.
Tools and Resources You Need to Read Plumbing Plans
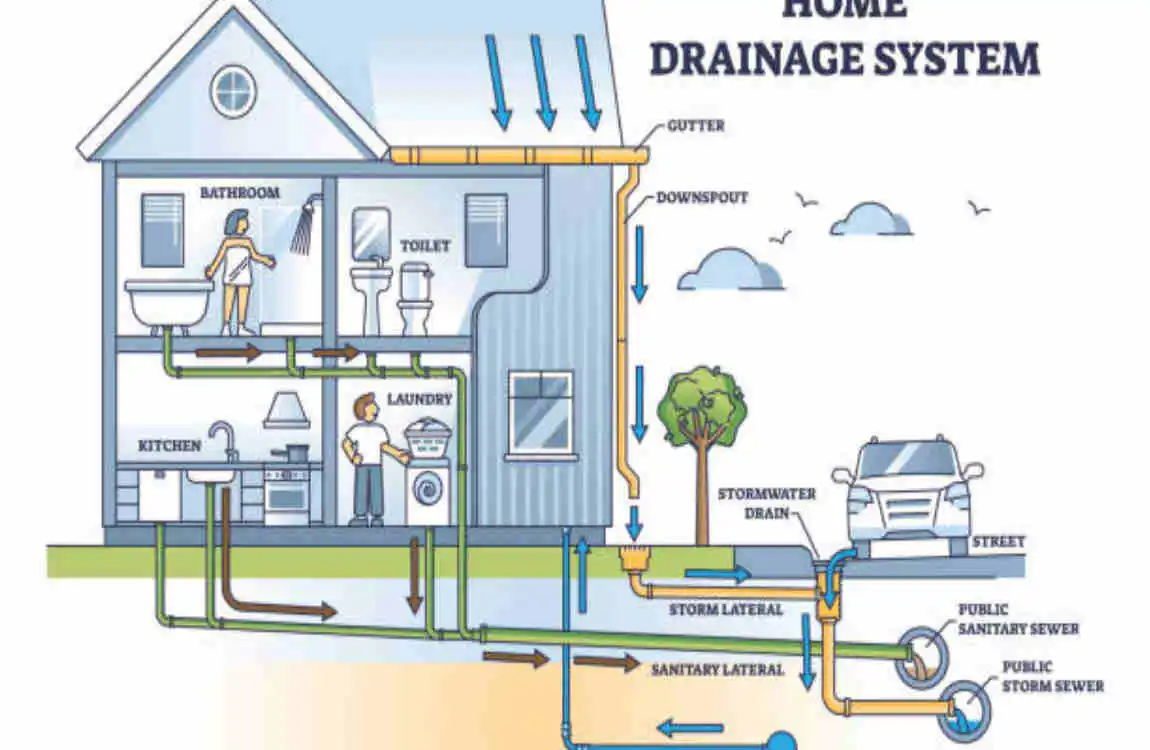
You don’t need an engineering degree to study plumbing plans—but having the right tools and references makes your job a lot easier.
Fundamental Tools for Accurate Interpreting
Think of yourself as a plumbing detective. These tools help you connect the dots:
- Scale ruler: Compare measurements between your plan and an actual setup.
- Highlighters: Color-code supply lines, drains, or fixtures to avoid confusion.
- Field notes: Jot down questions when things aren’t clear.
- Laser pointer (laser level): Fantastic for aligning plans with physical spaces in existing homes.
If you’re working digitally, a PDF annotation tool like Bluebeam or Adobe Acrobat offers layers, highlighting features, and measurement tools that mimic real-world tools.
Challenge: Strange Symbols or Code Jargon
You’re staring at a tiny triangle labeled “C.O.”—what does it mean? “Cleanout”? Yep! These shortcuts may seem baffling at first, but they become consistent once you learn them.
Solution: Keep a smartphone nearby with access to an online symbol dictionary. If you’re at a job site, take a photo and annotate the symbol later. Join plumbing forums, such as the DoItYourself.com community, for quick answers.
Challenge: Missing or Vague Details
house Plans might leave you hanging—missing component sizes, unclear directions, or omitted fixture quantities.
Remedy: Never assume. This is where collaboration shines. Reach out to the architect or engineer to clarify. Better safe than sorry.
Cross-Referencing Blueprints: Smart Tips
house Plumbing doesn’t operate in isolation. Cross-reference architectural plans for wall types—solid beams versus drywall—because cutting through the wrong obstruction could be dangerous. HVAC and electrical plans also flag competing lines or obstructions (e.g., pipes buried behind electrical panels).
Pro tip: If you’re unsure about a plan, overlay digital copies on-screen to catch clashes early.
Practical Examples and Case Studies
Theory is helpful, but how does this unfold in real life? Let’s explore two plumbing plans to illustrate key principles.