The United States legislative process itself begins at the dais in the House chambers. It is the nerve center of the House of Representatives, a place where key decisions get made, arguments get shepherded, where legislative history gets written. For people less attuned to the complexities of the U.S. government, the dais might seem like just another elevated platform. But its duties, its history and the people who inhabit it help tell the tale of its significance.
By the end, you’ll have a deep knowledge of why the dais is both central to how the House operates and a symbol of American democracy.
A Step Back in Time: Tracing the Origins and Evolution of the House Dais

The history of the dais is tied to the history of the United States and its legislative processes. Its roots date back to the first Congress following the ratification of the Constitution in1789. The dais was fundamentally built as a space for the Speaker of the House and other officials to act as hosts for debates, votes and other legislative matters.
The Early Design and Purpose
In its original design, the dais was a plain structure — a raised platform to put the Speaker and other officers in view of members of Congress. This design places House chamber within a direct line of communication with presiding officer which helped enable the efficient order of legislative business.
Evolution Over Time
Over the years, the dais underwent both functional and aesthetic changes. Its evolution was driven by changing legislative requirements, architectural fashions and symbolic significance. For instance:
- During the 19th Century, the dais grew more ornate in design, echoing the increasing elevation of the House of Representatives.
- Technological advancements like electronic voting led to structural updates as well.
Renovations and Modifications
Historically, the dais has been updated to reflect the requirements of a 21st-century Congress. For example:
- For the mid-20th century, updates included audio systems that would improve communication across the chamber.
- Renovations after the year 2000 included digital displays and voting devices, keeping the dais functional in an age of technological innovation.
This evolution of the dais speaks volumes about its role as a pivotal epicenter of the House chambers.
The Pyramid Scheme: Decoding the Three Layers of the House Dais

The dais of House chambers is a structure that helps facilitate the basic functions for House members. Three tiers of Deputy Presidents surround him as figures of beauty around a pyramid, but they also have functional boundaries — functional blocks — which work directly in favour of the legislative process.
Layout and Function: The Three Tiers
The dais consists of three different tiers, each section serving its own function:
The Top Tier:
- This is the seat of the Speaker of the House, the chamber’s presiding officer. Seated at the rostrum high above the floor, Speaker presides over debate, maintains decorum, and embodies the authority of the House.
- Because it is placed at the center of the action, the Speaker’s chair symbolizes leadership and impartiality.
The Middle Tier:
- This is where people like the Clerk of the House and the Parliamentarian reside. These officials help ensure that proceedings run seamlessly, advising on rules and overseeing administrative tasks.
- Timekeepers and assistants might also fall into this tier, responsible for procedural aspects like time on debate.
The Bottom Tier:
- The basement level is occupied by the Sergeant at Arms, Journal Clerks and other personnel who provide a supporting function of preserving order and keeping a record of legislative proceedings.
Materials and Symbolism
Yoran then elaborates: the dais is made up of high-grade materials, like wood and marble, which are selected not only for their durability but also for what they represent. Intricate carvings and details, for instance, often include national symbols like the American eagle or olive branches, representing strength and peace.
Inner Circle and Outer Circle Arrangements
Sitting at the center of the House chamber, the dais was built to attract attention. The surface stands clear of the floor, allowing everyone to see everyone else — a visual metaphor for its status at the head of the authority table.
The dais is designed to serve a dual purpose, being both functional and a symbol of legislative power.
Who Sits Where? A Guide to the Players on the House Dais

The dais is not merely a stage — it is the seat of some of the most important figures in the legislative process. Everyone sitting on the dais is critical to the functioning of the House of Representatives.
Speaker of the House
The most prominent person on a dais is the Speaker of the House. As the presiding officer, the Speaker:
- Controls debates and makes sure that proceedings are conducted according to the preestablished rules.
- Serves in an official capacity to represent the House, as well as act as a prominent player in the legislative process.
- Seats at the center of the top tier, indicating their leadership role.
Clerk of the House
The House Clerk is responsible for:
- No more certifying bills or recording their legislative activity.
- All about delivering official messages to the Senate.
- Because the Clerk is seated on the middle tier, he or she serves a critical administrative function.
Parliamentarian
The Parliamentarian serves as a consultant on the House’s complicated rules and procedures. On the middle tier, they help the Speaker make sure that debates and votes run according to established rules.
Sergeant at Arms
The Sergeant at Arms is responsible for security and orderly proceedings in the chamber. However, though they may not always be at a seat, their location near the dais reinforces their duty to maintain decorum.
Journal and Tally Clerks
These clerks handle:
- Attending each session and writing the minutes
- Street parlance soothsayer for technology of electronic votes.
Official Reporters
The official transcribers capture everything that happens on the floor, to be entered into the Congressional Record. “Being seated close to the dais, there’s no way to miss a word spoken during proceedings.
- Everyone on the dais helps the House run smoothly so we can get our work done.
- Finding Meaningfulness Beyond a Seat: The Functional Importance of the Dais
More Than Just a Seat: Exploring the Functional Significance of the Dais
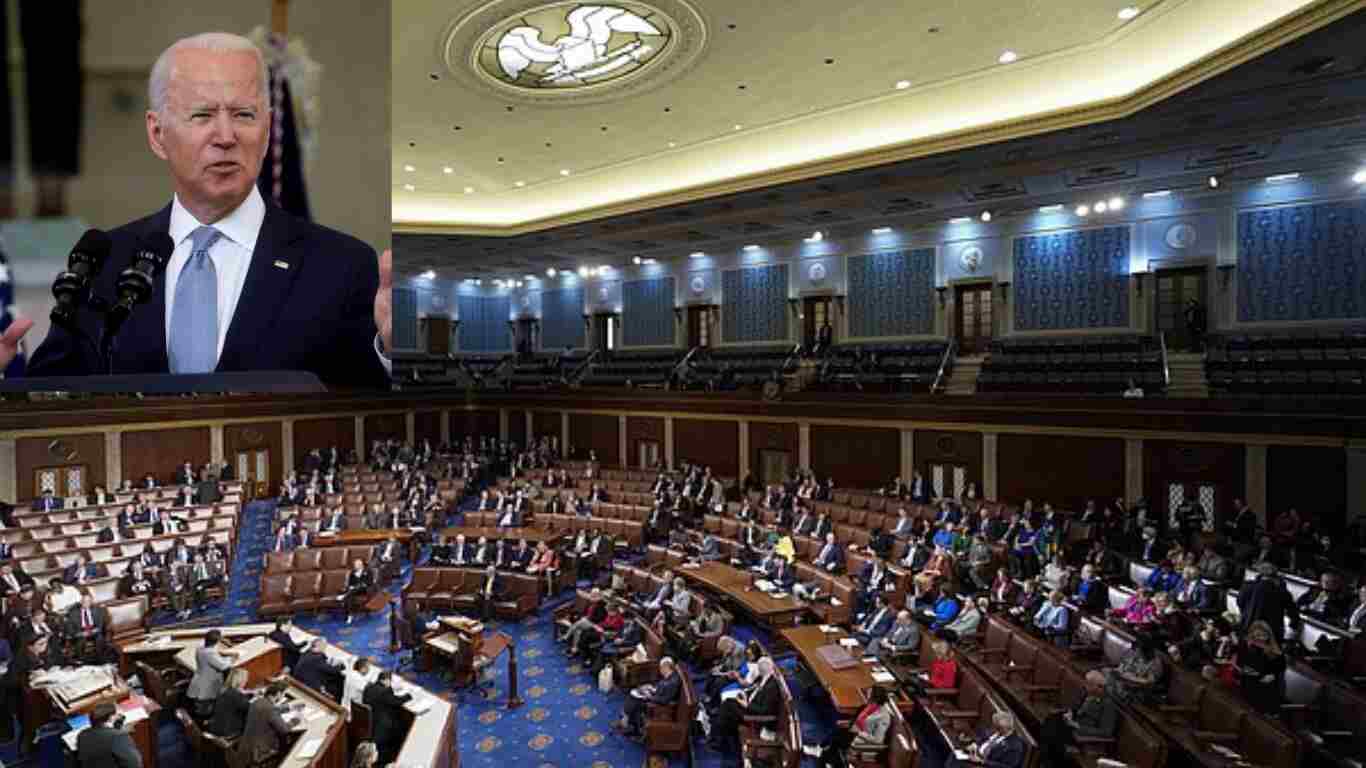

Conducting Legislative Activities
The dais is command central for:
- Overseeing debates and discussions in the House chamber.
- Getting votes lined up and watching the process.
- Helping enable communication between officials and lawmakers.
Symbolism and Authority
- Beyond its utilitarian roles, the dais symbolizes:
- By the power of the Speaker and the House of Representative.
- The democratic principles of order, fairness, and accountability.
Key Events and Moments
The dais has been home to countless historic moments, from major votes to landmark legislative decisions. These moments reaffirm its vital role in American democracy.
The Dais Decoded: Our Focus on a Central Element in the House Chambers
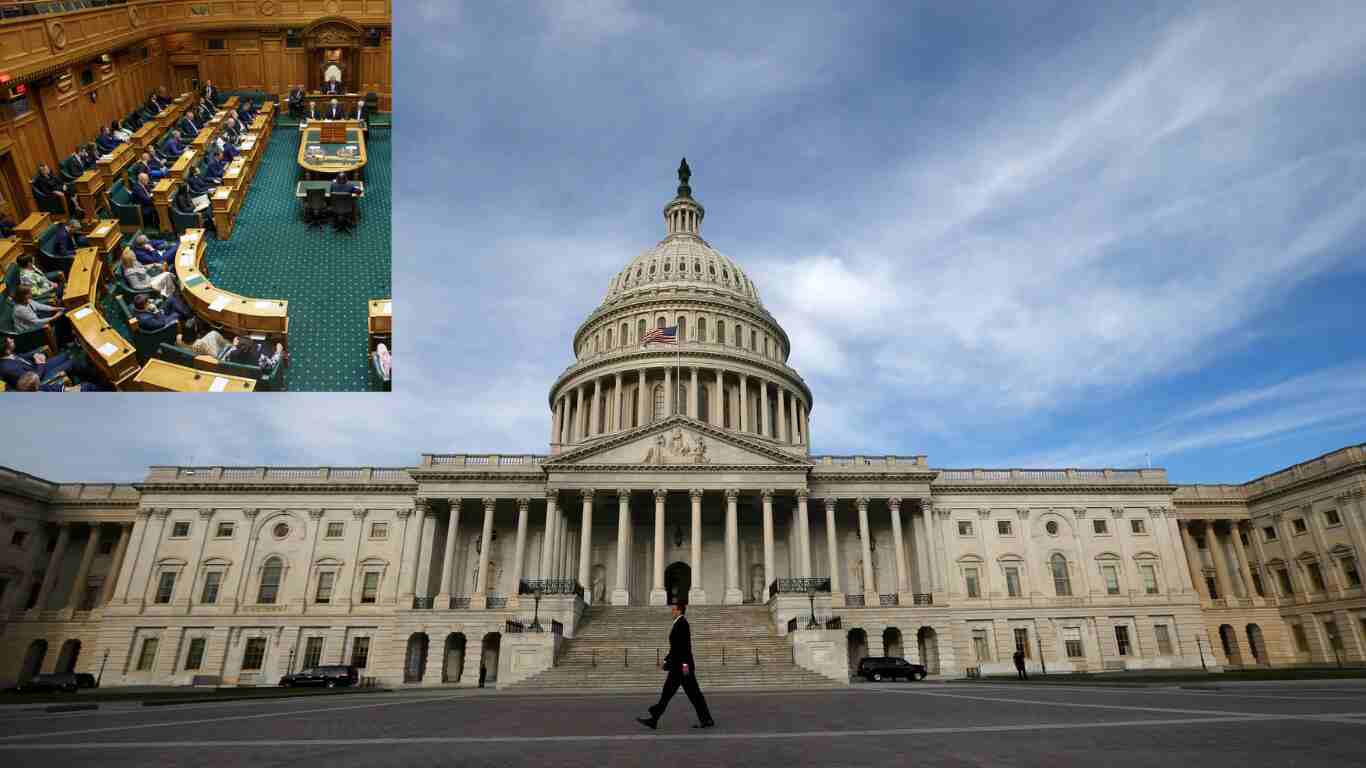
The dais in the House chambers is not just a raised platform—it is a symbol of authority, a hub of legislative activity, and a testament to the enduring principles of American democracy. The History, Structure, Key Individuals and Importance of the Executive Branch:– A deeper understanding of how the U.S. government works Deliveryhug a deeper understanding of how the U.S. government works.
Whether you’re a student of politics, a history buff or simply curious about how the House of Representatives works, knowing the dais provides a glimpse of how the legislative process unfolds. It serves as a reminder of the delicate dance between the past and the present that is the hallmark of the U.S. government.
So the next time you witness a session of Congress in action, take a moment to appreciate the dais — towering high above as the nexus of the House chambers and the foundation of American democracy.
Also read (tribeca house nyc.)
